More than 60 percent of australian businesses have experienced a data breach in the last year, showing just how vital strong protection strategies are for sensitive client information. For IT managers in Brisbane’s financial sector, keeping up with evolving australian regulations is more than just paperwork—it directly impacts your credibility and operational safety. This guide delivers practical clarity on what defines sensitive data and outlines proven tactics for compliance and risk reduction tailored to financial services environments.
Table of Contents
- Defining Sensitive Data And Key Concepts
- Types Of Sensitive Data In Finance
- Legal Frameworks And Compliance In Australia
- Essential Data Security Controls And Technologies
- Roles, Duties And Costly Risks For Firms
- Common Compliance Pitfalls To Avoid
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Understanding Sensitive Data | Brisbane businesses must recognise and classify sensitive data to ensure compliance and robust cybersecurity measures. |
| Legal Compliance | Adherence to the Privacy Act and Data Availability and Transparency Act is critical for protecting sensitive information and avoiding penalties. |
| Data Security Controls | Implementing the Essential Eight mitigation strategies is essential to safeguard sensitive data against evolving cyber threats. |
| Avoiding Compliance Pitfalls | Regular audits, staff training, and proper documentation are fundamental to prevent common compliance failures and minimise risks. |
Defining Sensitive Data And Key Concepts
Sensitive data represents confidential information that requires specialised protection mechanisms to prevent potential misuse or unauthorised access. For Brisbane businesses operating in regulated sectors like finance and healthcare, understanding sensitive data classifications is fundamental to maintaining robust cybersecurity practices. Personal information safeguards establish clear guidelines about what constitutes protected digital assets.
Under Australian legal frameworks, sensitive data encompasses several critical categories that demand heightened security protocols. These include personal identifiers such as tax file numbers, health records, financial account details, biometric information, and demographic data that could potentially enable individual identification. The DATA Scheme safeguards emphasise transparent processes for managing such information, highlighting the importance of purpose-driven data handling and strict accreditation standards.
Key characteristics that define sensitive data typically involve potential risk factors if compromised. This includes information that could enable identity theft, financial fraud, personal profiling, or expose an individual’s private characteristics. Specific examples range from medical histories and genetic information to political affiliations, sexual orientation, religious beliefs, and racial background. Organisations must implement comprehensive risk management strategies that categorise, protect, and restrict access to these highly confidential data elements.
The table below summarises key sensitive data categories and their associated risk factors for Brisbane businesses.
| Sensitive Data Category | Potential Risk if Compromised | Example Use in Business |
|---|---|---|
| Health records | Medical identity theft, blackmail | Healthcare service provision |
| Financial account details | Fraudulent transactions, theft | Banking and payment processing |
| Biometric information | Identity fraud, unauthorised access | Employee authentication systems |
| Demographic data | Unauthorised profiling, discrimination | Customer segmentation |
| Tax file numbers | Tax fraud, identity theft | Employee payroll and reporting |
Pro tip:Conduct a quarterly audit of your sensitive data inventory to ensure ongoing compliance and identify potential exposure risks before they become critical security challenges.
Types Of Sensitive Data In Finance
Financial institutions in Brisbane face complex challenges when managing sensitive data types that require stringent protection and controlled access. Open Banking regulations have significantly transformed how financial organisations categorise and handle confidential information, establishing clear frameworks for data management and privacy.
The primary categories of sensitive financial data encompass several critical domains. These include personal contact details, financial transaction histories, account balances, credit ratings, and comprehensive banking product information. Australian Privacy Principles provide explicit guidance on managing these sensitive information types, highlighting the importance of maintaining consumer privacy and preventing potential misuse.

Moreover, sensitive financial data extends beyond basic transaction records to include more nuanced information such as financial hardship indicators, insolvency details, investment portfolios, and comprehensive credit histories. Each data type carries unique risk profiles and requires tailored protection strategies. Financial organisations must implement robust classification systems that differentiate between varying levels of data sensitivity, ensuring appropriate security protocols are consistently applied across different information categories.
Pro tip:Develop a comprehensive data classification matrix that assigns specific security levels and handling protocols to each type of sensitive financial information.
Legal Frameworks And Compliance In Australia
Australian organisations must navigate a complex landscape of legal requirements designed to protect sensitive data and ensure robust cybersecurity practices. Privacy Act foundations establish comprehensive guidelines that govern how businesses handle personal and confidential information, creating a structured approach to data protection across various sectors.
The primary legislative mechanisms driving data protection in Australia include the Privacy Act 1988, which embeds the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), and the more recent Data Availability and Transparency Act of 2022. These frameworks provide explicit mandates for data handling, outlining precise requirements for collection, storage, usage, and disclosure of sensitive information. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies must adhere to these strict regulations, implementing comprehensive compliance strategies that protect individual privacy rights.
Compliance involves multiple layers of legal obligations, including mandatory data breach notification requirements, strict consent mechanisms for data collection, and rigorous security standards. Organisations must develop internal policies that not only meet but exceed these legislative requirements, creating robust governance structures that proactively manage potential risks. This involves regular audits, comprehensive staff training, and sophisticated technological safeguards that ensure ongoing protection of sensitive information.
Pro tip:Conduct an annual comprehensive review of your organisation’s data protection policies to ensure alignment with the latest legislative updates and regulatory requirements.
Essential Data Security Controls And Technologies
Australian businesses must implement comprehensive cybersecurity controls to protect sensitive information from evolving digital threats. Essential Eight mitigation strategies provide a robust framework for organisations seeking to establish baseline protection mechanisms across their digital infrastructure.
The core technological controls fundamental to data security include multifactor authentication, application whitelisting, regular system patching, and sophisticated access management protocols. These technologies work synergistically to create multiple layers of defense, preventing unauthorized access and minimizing potential vulnerability points. Organisations must adopt a holistic approach that combines technical controls with comprehensive user training and ongoing risk assessment strategies.
Moreover, privacy requirements demand that businesses implement advanced encryption technologies, secure network configurations, and continuous monitoring systems. This includes deploying endpoint protection platforms, implementing robust intrusion detection mechanisms, and establishing secure data transmission protocols. Critical technologies such as virtual private networks (VPNs), advanced firewall configurations, and secure cloud storage solutions provide essential protection for sensitive organisational data.
Pro tip:Conduct quarterly comprehensive security audits that systematically evaluate and update your organisation’s technological defense mechanisms against emerging cyber threats.
Roles, Duties And Costly Risks For Firms
Australian businesses face increasingly complex legal obligations surrounding data protection and corporate governance. Corporate director responsibilities extend far beyond traditional management expectations, creating significant personal and organisational liability for data security and compliance failures.
Key roles within organisations must establish clear accountability for sensitive data management. This includes executive leadership defining strategic data protection frameworks, IT managers implementing technical controls, and compliance officers ensuring ongoing regulatory adherence. Each role carries specific responsibilities: executives must provide strategic direction, IT professionals must design and maintain secure infrastructure, and compliance teams must continuously monitor and update protection mechanisms to address emerging cyber risks.
The potential consequences of neglecting these responsibilities are substantial. People risk management highlights that organisational failures can result in severe financial penalties, reputational damage, legal sanctions, and potential operational disruptions. Firms may face significant financial consequences ranging from regulatory fines to potential legal actions, with individual directors potentially facing personal liability for systemic compliance failures.
Pro tip:Implement a comprehensive risk accountability matrix that clearly defines data protection responsibilities for each organisational role, ensuring transparent and measurable compliance mechanisms.
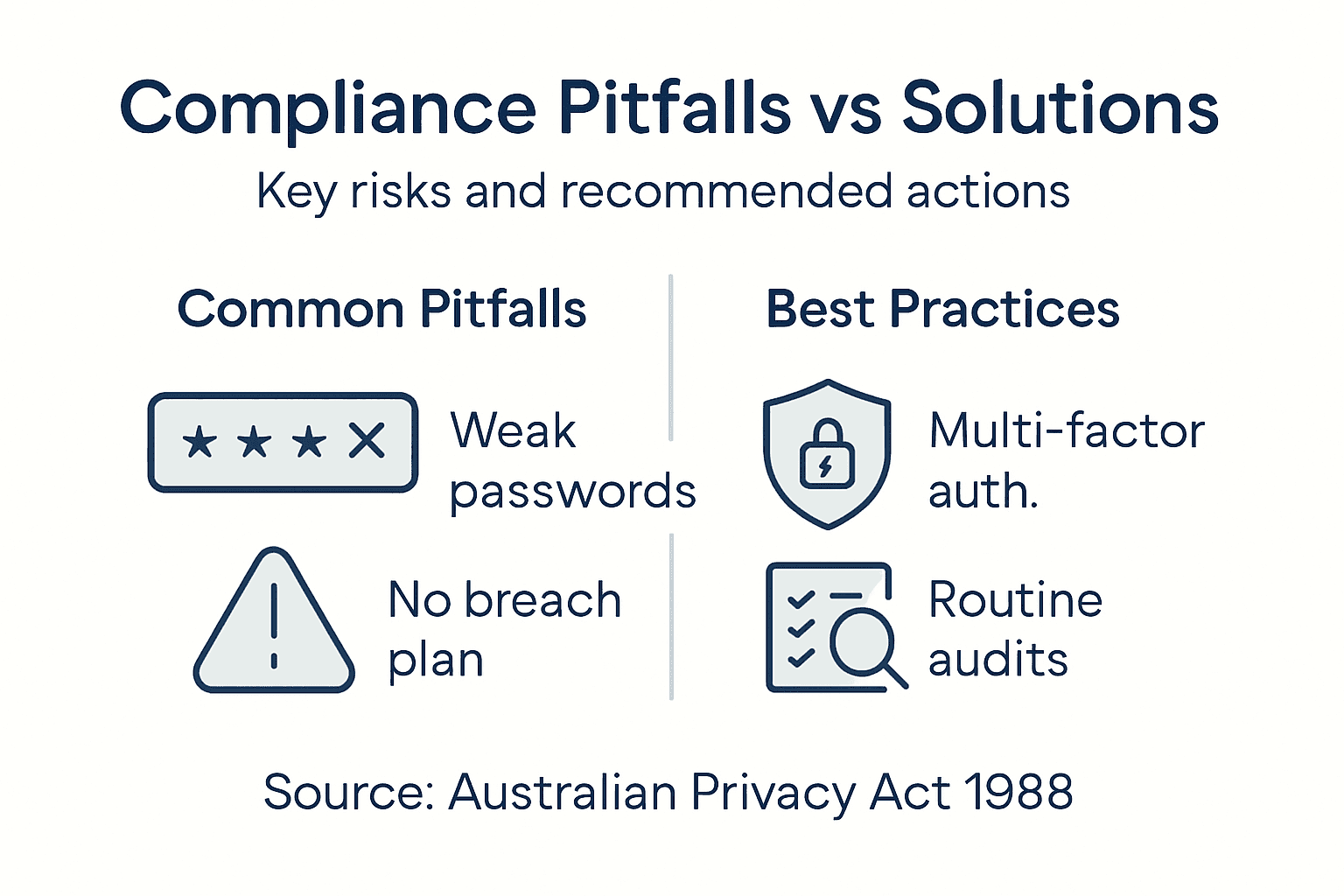
Common Compliance Pitfalls To Avoid
Navigating sensitive data protection requires a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating potential compliance risks. Compliance and enforcement frameworks highlight critical vulnerabilities that Brisbane firms must address to maintain robust data security standards.
Organisations frequently encounter several systemic compliance pitfalls that can compromise their data protection strategies. These include inadequate staff training, inconsistent risk assessment processes, poor documentation of data handling procedures, and failure to implement comprehensive monitoring mechanisms. Businesses often underestimate the complexity of maintaining continuous compliance, particularly when dealing with evolving technological landscapes and shifting regulatory requirements.
Significant breach management represents another critical area where organisations frequently stumble. Significant breach obligations demand timely reporting, thorough root cause analysis, and structured remediation plans. Common mistakes include delayed incident reporting, insufficient investigation depth, and reactive rather than proactive risk management approaches. These oversights can result in substantial financial penalties, reputational damage, and potential loss of customer trust.
The table below contrasts common compliance pitfalls with best-practice mitigation approaches.
| Compliance Pitfall | Consequence | Recommended Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Inadequate staff training | Increased risk of breaches | Regular security awareness sessions |
| Poor documentation of data processes | Difficulty proving compliance | Maintain clear, up-to-date records |
| Inconsistent risk assessments | Missed vulnerabilities | Schedule systematic risk reviews |
| Delayed breach reporting | Heavier fines, reputational loss | Set up immediate incident protocols |
Pro tip:Develop a comprehensive compliance checklist that includes quarterly review cycles and mandatory staff training sessions to systematically identify and address potential regulatory vulnerabilities.
Strengthen Your Sensitive Data Protection with Brisbane’s Trusted IT Partner
Sensitive data breaches can lead to severe legal repercussions, financial losses, and reputational damage for Brisbane businesses. This article highlights critical challenges such as managing sensitive data classifications, meeting stringent Australian compliance frameworks, and implementing robust data security controls. At IT Start, we understand the urgent need for tailored cybersecurity solutions that secure financial, health, and personal data while helping you meet regulatory obligations.
Our local expertise and certified standards empower small to medium enterprises to mitigate risks through proactive managed IT support, cloud solutions, and advanced cybersecurity. Don’t wait for a costly data breach or compliance failure. Take control today by getting a free assessment with IT Start. Discover how our customised strategies can ensure ongoing compliance and safeguard your sensitive data.
Start safeguarding your business now with a trusted Brisbane IT partner. Contact us via our dedicated page or learn more about how we help firms comply with sensitive data protection regulations at IT Start Contact. Protect your organisation’s future by acting now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered sensitive data in my business?
Sensitive data encompasses confidential information that requires protection, including personal identifiers like tax file numbers, health records, financial account details, and biometric information. Understanding these categories is crucial for compliance and safeguarding against potential risks.
Why is it important for my business to protect sensitive data?
Protecting sensitive data is essential to prevent identity theft, financial fraud, and breaches of privacy. Failing to secure this information can lead to severe legal penalties, financial loss, and reputational damage.
What are the main regulations governing sensitive data protection?
In Australia, the primary regulations include the Privacy Act 1988, which incorporates the Australian Privacy Principles, and the Data Availability and Transparency Act of 2022. These frameworks outline the requirements for data collection, storage, usage, and disclosure, necessitating compliance from various sectors.
How can my business implement effective data security controls?
To implement effective data security controls, consider using multifactor authentication, regular system patching, advanced encryption, and secure network configurations. Regular audits and employee training on cybersecurity best practices are also critical to maintaining a robust security posture.
Recommended
- How to Secure Your Data for Brisbane Businesses Effectively – IT Start
- What Is Data Loss Prevention – Protecting Brisbane Businesses – IT Start
- 7 Essential Data Protection Tips for Brisbane Businesses – IT Start
- Is My Data Safe? Protecting Brisbane SMEs in 2026 – IT Start
- Enhanced Security and Protection for Sensitive Data Websites | WPCTO Case Study



