Over 43 percent of australian data breaches now affect small to medium businesses, leaving financial and legal firms in Brisbane more exposed than ever. As digital transactions and sensitive client records become the norm, cyber attacks pose a direct threat to operations and trust. This guide breaks down practical cybersecurity strategies, equipping you with clear steps to safeguard your business against increasing online risks.
Table of Contents
- Cyber Security Explained For Queensland SMEs
- Major Threats And Types Facing Brisbane Businesses
- How Cyber Safeguards Work In Practice
- Legal Obligations And Compliance In Queensland
- Risks, Penalties, And Costly Mistakes To Avoid
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Cyber Security is Essential | Understanding and implementing cyber security measures is critical for Queensland SMEs to protect against sophisticated online threats. |
| Proactive Strategies Required | Businesses should adopt multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, and staff training to enhance their cyber resilience. |
| Compliance is Crucial | The Cyber Security Act 2024 mandates reporting of cyber incidents, necessitating robust governance and employee training to avoid penalties. |
| Ongoing Risk Management | Regular audits and a culture of cybersecurity awareness can help identify vulnerabilities and prevent costly breaches. |
Cyber security explained for Queensland SMEs
Cyber security represents a critical shield for small and medium businesses across Queensland, protecting digital assets from increasingly sophisticated online threats. With digital technologies becoming fundamental to business operations, understanding cyber security fundamentals has shifted from optional to essential. Queensland businesses face complex digital risks that demand proactive and strategic protection approaches.
The Queensland government recognises these challenges, launching a comprehensive cyber security strategy targeting SME digital resilience. This initiative acknowledges that small businesses are particularly vulnerable to cyber attacks, often lacking robust technological defences. Cyber criminals frequently target organisations with limited security infrastructure, viewing them as easier entry points into broader networks.
Qld SMEs must understand that cyber security isn’t just about technology – it’s about creating a holistic protective culture. Key defensive strategies include implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software, conducting staff training on recognising phishing attempts, and developing incident response plans. The Queensland government’s $15 million support program provides free tools and resources specifically designed to help local businesses strengthen their digital defences.
Pro tip:Conduct a free cyber security assessment every six months to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they become critical security risks.
Major threats and types facing Brisbane businesses
Brisbane businesses face a complex and evolving landscape of cyber threats that can potentially devastate organisational operations. Sophisticated cyber attacks continue to emerge, targeting businesses of all sizes with increasingly advanced techniques designed to exploit technological vulnerabilities.
The primary cyber threats confronting Brisbane enterprises include phishing, ransomware, business email compromise, and supply chain attacks. Phishing remains particularly insidious, with cybercriminals crafting deceptive emails and messages that trick employees into revealing sensitive information or inadvertently installing malicious software. Ransomware attacks represent another critical risk, where criminal actors encrypt critical business data and demand payment for its release, potentially causing significant operational disruption and financial damage.
Small and medium enterprises are especially vulnerable due to limited cybersecurity resources and potentially less sophisticated defence mechanisms. Hackers often view these organisations as easier targets, exploiting gaps in technological infrastructure and employee awareness. Common attack vectors include unpatched software vulnerabilities, weak password protocols, inadequate network security, and insufficient staff training on recognising potential security risks.
Here’s a summary of common cyber threats and their specific business impacts for Brisbane SMEs:
| Threat Type | Unique Characteristics | Typical SME Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Deceptive emails targeting staff | Data theft, financial loss |
| Ransomware | Encrypts business files for ransom | Business operations halted |
| Email Compromise | Hijacks business communications | Unauthorised payments, reputation damage |
| Supply Chain Attack | Exploits third-party vendors | Disruption across partners, trust issues |
Pro tip:Implement mandatory quarterly cybersecurity awareness training for all staff members to dramatically reduce the likelihood of successful social engineering attacks.
How cyber safeguards work in practice
Cyber safeguards represent a multilayered defence strategy designed to protect Brisbane businesses from increasingly sophisticated digital threats. Queensland cyber security strategies emphasise proactive protection through integrated technological and human-centric approaches that address potential vulnerabilities across organisational systems.
Effective cyber safeguards typically involve multiple complementary components. Network security forms the foundational layer, incorporating firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access. Employee training acts as a critical human firewall, teaching staff to recognise potential phishing attempts, maintain strong password practices, and understand their role in maintaining organisational digital security. Regular software updates, vulnerability assessments, and robust access control mechanisms further strengthen these protective measures.

Implementation requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond technological solutions. Businesses must develop detailed incident response plans, conduct periodic security audits, and create a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. This involves understanding potential threat vectors, maintaining up-to-date threat intelligence, and developing resilient systems that can quickly detect, respond to, and recover from potential cyber incidents.
Pro tip:Conduct monthly simulated cyber attack drills to test and improve your organisation’s incident response capabilities and employee awareness.
Legal obligations and compliance in Queensland
Brisbane businesses must navigate a complex landscape of cybersecurity legal requirements that are rapidly evolving to address digital threats. Cyber Security Act 2024 introduces stringent compliance measures that fundamentally reshape how organisations approach digital protection and information security.
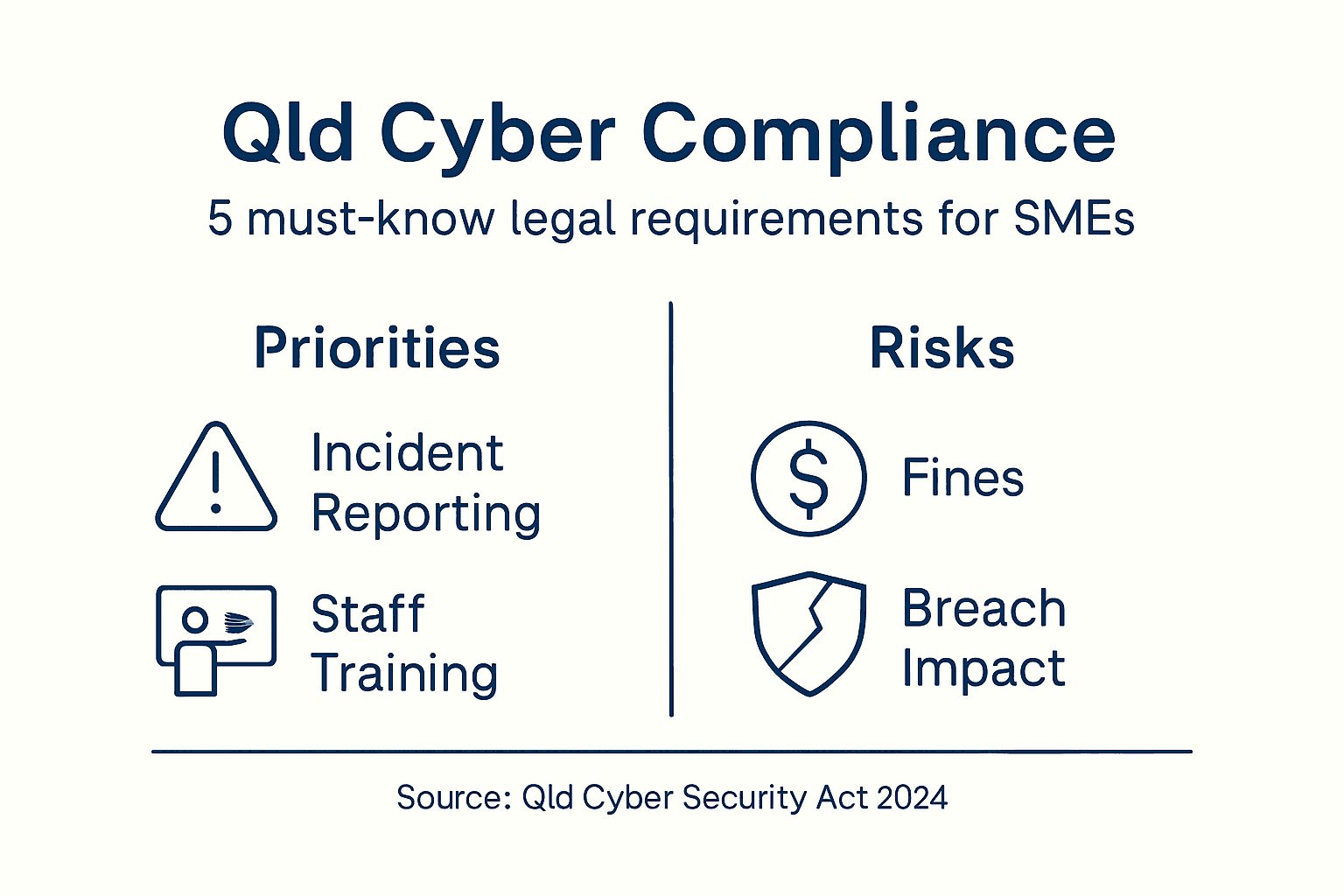
The legislative framework imposes significant mandatory reporting obligations on businesses, requiring them to disclose cyber incidents, ransomware payments, and potential data breaches within specified timeframes. Queensland enterprises must implement robust governance structures that demonstrate proactive risk management, including comprehensive documentation of cybersecurity policies, regular security assessments, and evidence of staff training programs. Non-compliance can result in substantial financial penalties and potential legal consequences that could dramatically impact an organisation’s reputation and operational continuity.
Key compliance requirements extend beyond mere technological solutions, demanding a holistic approach to cybersecurity. Businesses must develop and maintain detailed incident response plans, ensure appropriate data encryption methods, implement multi-factor authentication, and maintain rigorous access control mechanisms. The legislation emphasises the importance of creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness, where every employee understands their role in maintaining organisational digital resilience.
This table highlights major compliance requirements under the Cyber Security Act 2024 and their direct consequences for Queensland businesses:
| Compliance Requirement | Purpose | Consequence of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Mandatory incident reporting | Fast identification of cyber breaches | Large fines, reputational damage |
| Governance documentation | Shows risk management responsibility | Difficulty in legal defence |
| Staff cybersecurity training | Empowers employees as front-line defenders | Increased attack vulnerability |
| Data encryption & MFA | Protects sensitive information | Risk of severe data leakage |
Pro tip:Develop a comprehensive compliance checklist that maps your current cybersecurity practices against the latest Queensland and Australian regulatory requirements to identify and address potential gaps.
Risks, penalties, and costly mistakes to avoid
Brisbane businesses face significant financial and operational risks when neglecting cybersecurity best practices. Cybersecurity mistakes can expose organisations to devastating consequences that extend far beyond immediate technical vulnerabilities, potentially threatening entire business operations.
The most common and costly cybersecurity errors include weak password management, inadequate staff training, neglecting regular system updates, and failing to implement multi-factor authentication. These vulnerabilities create open doors for cybercriminals, enabling unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential financial fraud. Under the new Cyber Security Act 2024, businesses can face substantial penalties up to $94,000 for non-compliance, with additional reputational damage that can erode customer trust and market reputation.
Specific high-risk mistakes that Queensland businesses must proactively address involve overlooking insider threats, ignoring patch management, insufficient data encryption, and lack of comprehensive incident response plans. Small oversights can cascade into major security breaches, potentially compromising sensitive customer information, disrupting business operations, and triggering complex legal and financial repercussions. Organisations must adopt a holistic approach to cybersecurity, treating it as an ongoing strategic priority rather than a one-time technical implementation.
Pro tip:Conduct quarterly comprehensive cybersecurity audits that systematically review and update your organisation’s security protocols, identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Strengthen Your Brisbane Business Against Cyber Threats with IT Start
Queensland SMEs face growing cybersecurity challenges such as phishing, ransomware, and compliance demands detailed in the Cyber Security Advice – Protecting Brisbane Businesses article. Without robust cybersecurity safeguards and proactive risk management, businesses risk costly data breaches and legal penalties under the Cyber Security Act 2024. If your organisation struggles with limited resources, staff training gaps, or incident response planning this is a critical moment to act.
IT Start specialises in providing Brisbane-based businesses with tailored managed IT support and cybersecurity services that align perfectly with these challenges. Our local experts help you build multilayered defences including network security, employee training, and compliance frameworks that meet industry standards such as SMB 1001 Gold. Don’t wait for an attack to expose vulnerabilities that disrupt operations or damage your reputation.
Discover how IT Start can help you proactively protect your business with a free cyber security assessment and consultation. Take the first step towards enhanced digital resilience by contacting us at IT Start Contact today. Empower your team with a trusted local partner experienced in navigating Queensland’s complex cyber landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major cyber threats facing businesses today?
Brisbane businesses face significant threats including phishing, ransomware, business email compromise, and supply chain attacks. Each of these can cause severe operational disruption and financial loss.
How can I improve my business’s cyber security?
Implement multi-factor authentication, regularly update software, conduct staff training on phishing recognition, and develop incident response plans to strengthen your cyber security.
What are the legal obligations for businesses regarding cyber security?
Under the Cyber Security Act 2024, businesses must comply with mandatory reporting obligations for cyber incidents and data breaches, maintain governance documentation, and provide staff cybersecurity training.
What common mistakes should businesses avoid to prevent cyber attacks?
Common mistakes include weak password management, inadequate staff training, neglecting regular updates, and failing to implement multi-factor authentication. Addressing these can significantly reduce vulnerability to cyber attacks.
Recommended
- What Cyber Security Protects for Brisbane Businesses – IT Start
- Cyber Security Threats – What Brisbane Businesses Face – IT Start
- Cyber Security Risks – What Brisbane Businesses Face – IT Start
- 7 Key Cybersecurity Risks Examples Every Brisbane SME Should Know – IT Start
- Securing the Defense Industry: Tackling Cybersecurity in an Interconnected World



